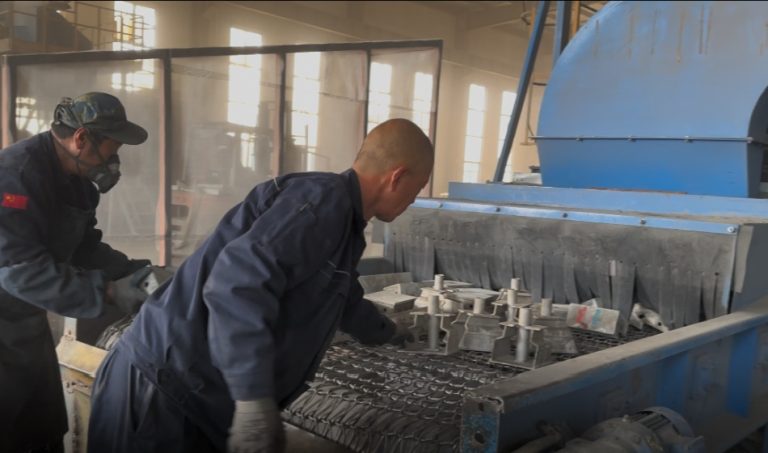
Scaffolding Maintenance Basics: Key Factors Influencing System Longevity
The Role of Preventive Maintenance in Steel Scaffolding Stability
Preventive maintenance plays a key role in steel scaffolding stability. It helps keep steady structural work on various building sites. Good maintenance starts with knowing how strain, shaking, weather, and ongoing weight affect scaffold parts. Regular upkeep of these steps stops a slow breakdown. This is true especially in tough jobs where scaffolding holds heavy moving weights and changing forces. Such routines also lower the chances of quick breakdowns. They create safer work areas. Plus, they boost overall system dependability. When scaffolding gets steady care, its firmness grows. Its working life lengthens. And job delays from gear problems drop a lot.
Material Behaviors of Q355 and Q235 Steel Under Repetitive Construction Loads
Material behaviors of Q355 and Q235 steel under repetitive construction loads strongly influence lifespan and safety outcomes. Q355 steel demonstrates higher yield strength and better fatigue resistance than Q235, making it suitable for heavy-duty scaffolding applications where cyclical forces are common. In contrast, Q235 steel performs effectively for lighter structural requirements but requires more frequent inspections due to its lower resistance to bending and impact stress. Both materials experience gradual wear over time, especially at welded joints, locking mechanisms, and contact surfaces. Understanding these behaviors allows teams to establish appropriate maintenance, inspection intervals, and component replacement planning, ensuring that steel scaffolding systems retain optimal performance in long-duration or high-rise projects.
Inspection Framework for Steel Scaffolding: Procedures, Criteria, and Risk Controls
Structured Daily and Weekly Inspection Checklists for Ringlock, Frame, and Tube-and-Coupler Systems
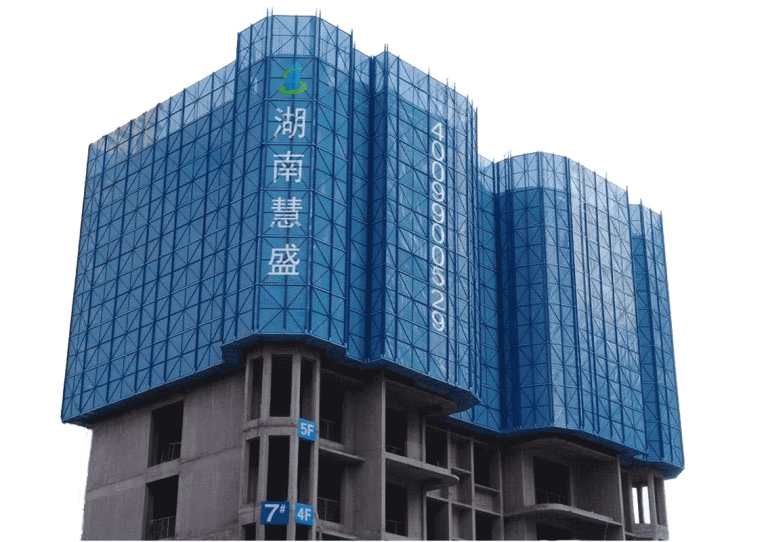
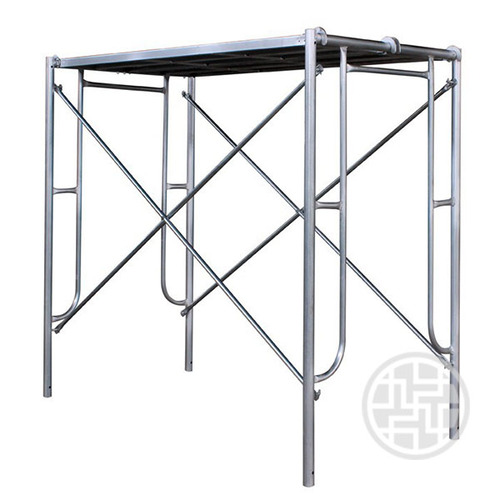
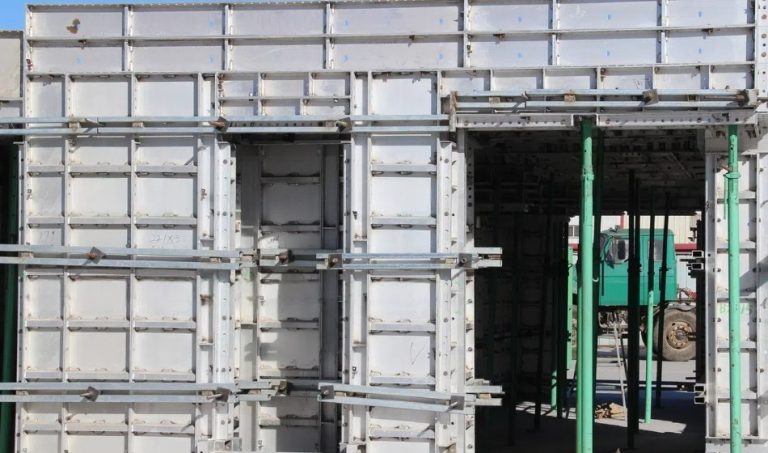
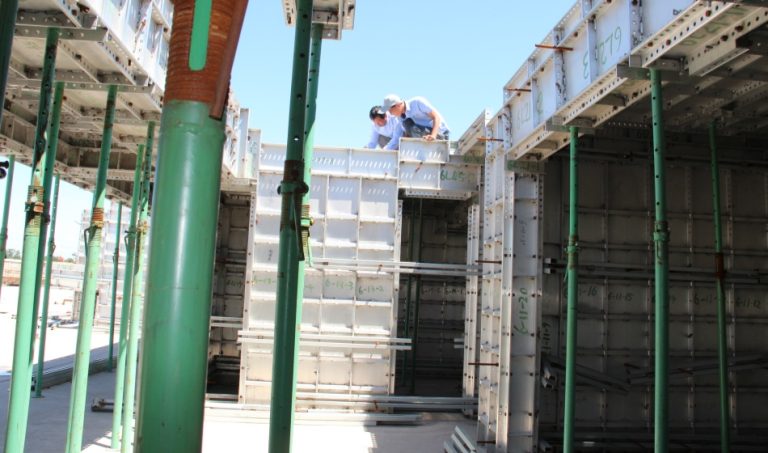
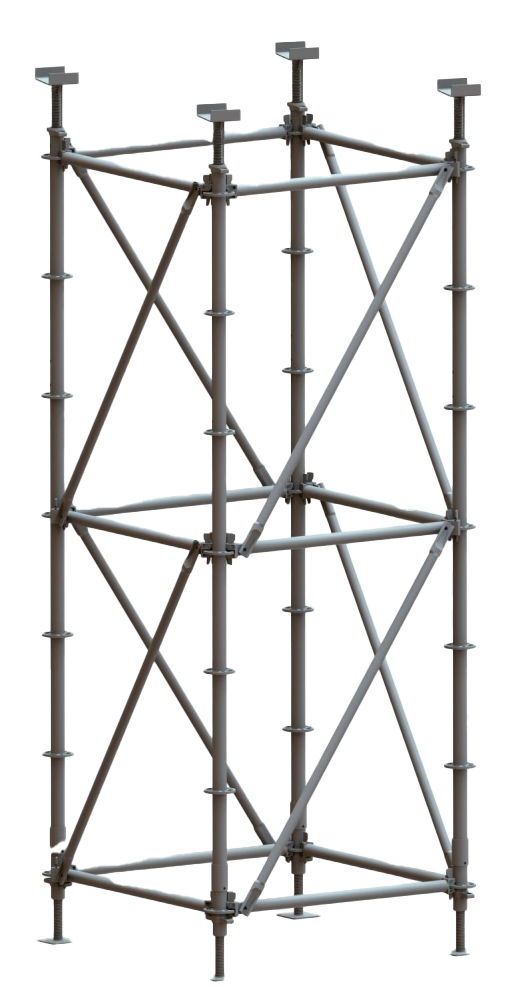
Structured daily and weekly inspection checklists for Ringlock, Frame, and Tube-and-Coupler systems set basic safety rules on any work site. Daily checks center on eye scans for bends, rust, lost pins, and wrong setup order. Weekly checks include broader reviews. These cover weight-hold tests, uprightness and line checks, and part-by-part confirmation of ledgers, standards, diagonal braces, and base jacks. For systems like the GOWE Ringlock -Gerüst System, checkers should verify rosettes, wedge connectors, and hot-dip galvanized surfaces. This ensures a steady mechanical fit. Following set steps builds regular habits. They cut risks and aid smooth job planning.
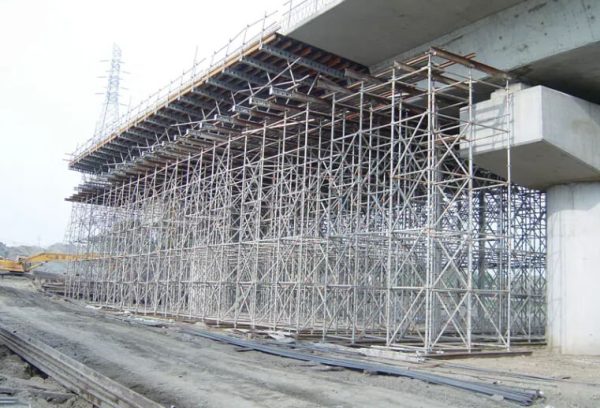

Identifying Mechanical Failures in Standards, Ledgers, Diagonal Braces, and Connection Points
Identifying mechanical failures in standards, ledgers, diagonal braces, and connection points helps building teams handle risks before frame weakness sets in. Mechanical issues often start with small signs. These include minor twists, less firmness, or uneven force spread across the scaffold frame. Standards might display local buckling. Ledgers can show bending tiredness from side weights. Diagonal braces may come loose from ongoing motion. This hurts overall strength. Spotting issues early needs a mix of eye checks, hand tests of links, and looking at past records. An active check mindset makes sure weak parts get swapped before they harm system wholeness.
Load-Bearing Evaluation and Replacement Thresholds for Critical Components
Load-bearing evaluation and replacement thresholds for critical components matter a lot. They help keep the full planned strength of scaffolding systems. Weight-hold ability can fall due to built-up tiny damage, rust, and link wear. Replacement limits should follow the build tolerance bounds set by makers and trade rules. Steady records aid past tracking and choices. They help judge if parts stay safe for reuse.
Deformation, Corrosion, and Surface Damage Indicators
Deformation, corrosion, and surface damage indicators give early alerts. They signal that parts may not hold set weights anymore. Checkers should look at bent or warped members, deep rust spread, weak welds, and thinner walls. This is key for Q235 parts that react more to rust and hits.
Joint Looseness, Locking Mechanism Wear, and Pin/Fastener Fatigue
Joint looseness, locking mechanism wear, and pin or fastener fatigue weaken the scaffold’s hold on shape under weight. Ringlock wedge pins, Gerüstkoppler, and connection sleeves must fit tightly without too much wiggle. Tired pins or worn couplers need quick replacement. This keeps the system firm and safe.
Maintenance Strategies That Extend Scaffolding Performance and Service Life
Cleaning and Surface Preservation for Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Components
Cleaning and surface preservation for hot-dip galvanized steel components significantly extends the life of scaffolding exposed to moisture, dust, and construction debris. Regular removal of concrete residue, mud, and corrosive agents prevents premature surface degradation. Hot-dip galvanization, used extensively in GOWE’s scaffolding systems, provides long-term corrosion protection, but proper cleaning ensures that zinc layers continue to function effectively.
Anti-Corrosion and Environmental Protection Practices for Q355/Q235 Systems
Anti-corrosion and environmental protection practices for Q355/Q235 systems cut dangers from weather, moisture, and chemical touch. Shield paints, dry keeping, air flow, and space from wet ground all slow rust growth. Q355 steel handles harming settings better. Yet both materials gain from regular surface care and setting control.
Storage, Handling, and Stacking Methods That Reduce Fatigue and Structural Stress
Storage, handling, and stacking methods that reduce fatigue and structural stress help keep frame wholeness between jobs. Parts should stack level, get proper support, and stay in clean, dry spots. Machine mishandling, like dropping or pulling parts, speeds up frame wear and link twists.
Component-Level Maintenance for Planks, Couplers, Jack Bases, and Bracing Units
Component-level maintenance for planks, couplers, jack bases, and bracing units makes sure each piece does its job without fault. Planks need checks for splits or layer splits. Couplers for thread wear and bends. Jack bases for screw-line soundness. And diagonal braces for straight form.
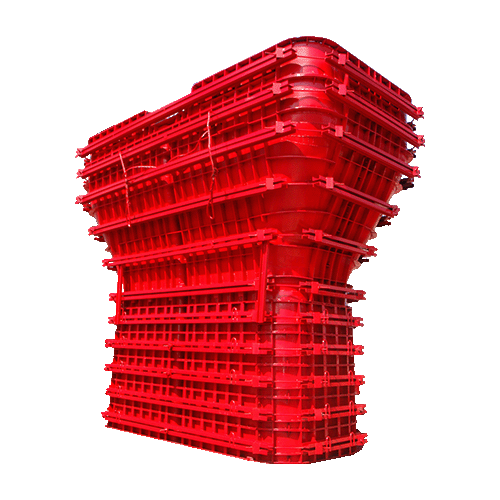
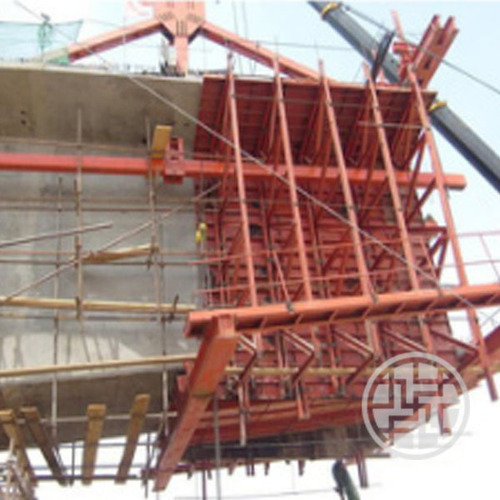
Lifecycle Management for Aluminum Beams Used With Scaffolding
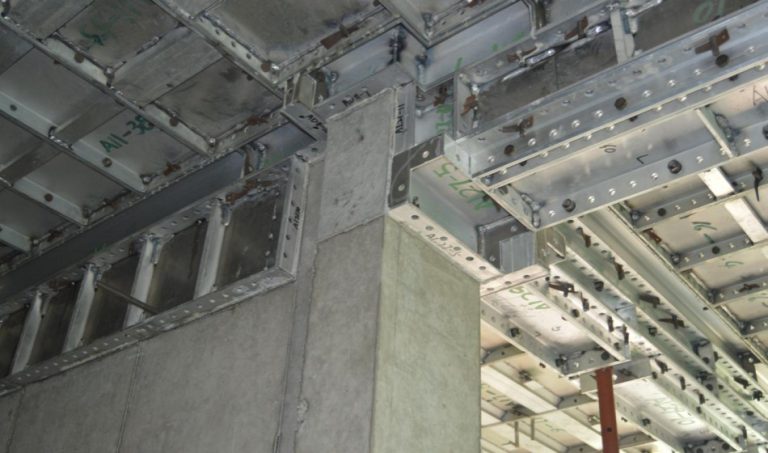
Lifecycle management for aluminum beams used with scaffolding matters because aluminum parts, like the GOWE 185 Aluminium Beam, work with steel frames under mixed weight settings. Checkers should watch fastener spots, beam straightness, and surface marks. These can change the weight spread.
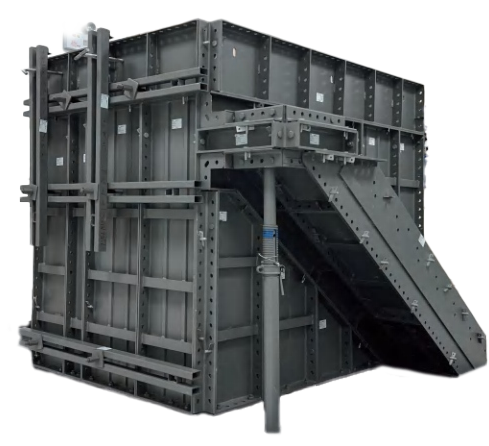
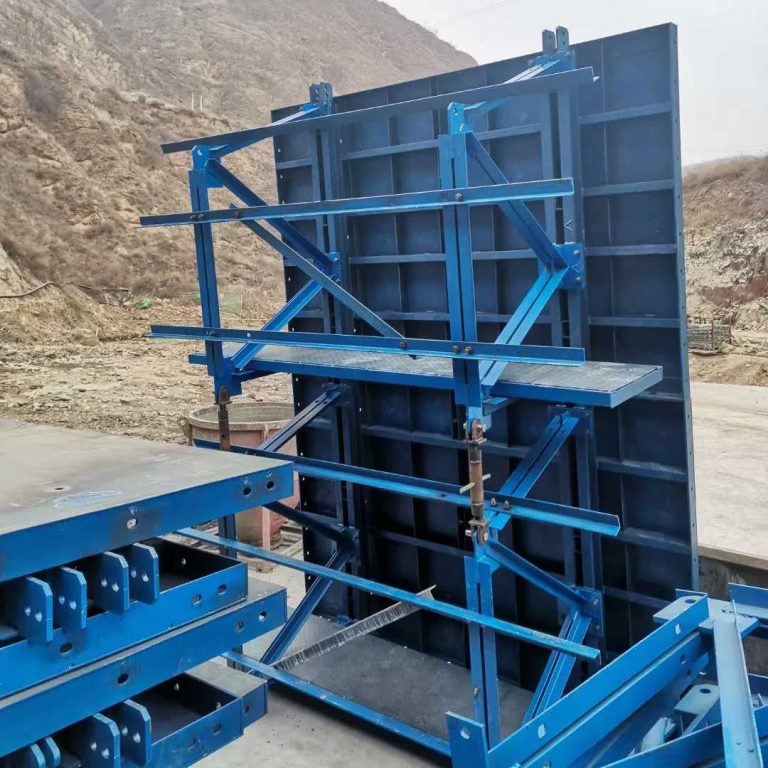
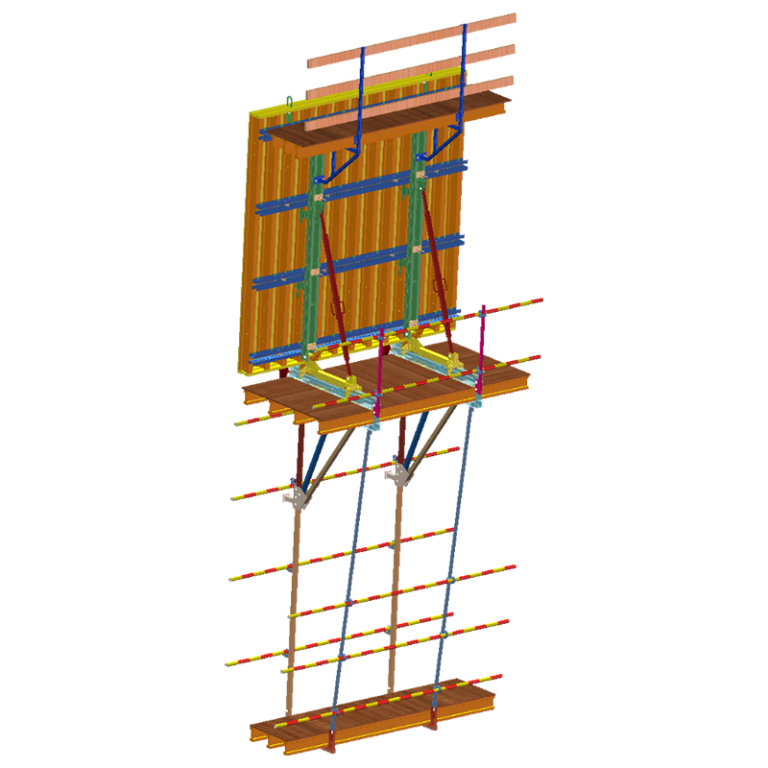
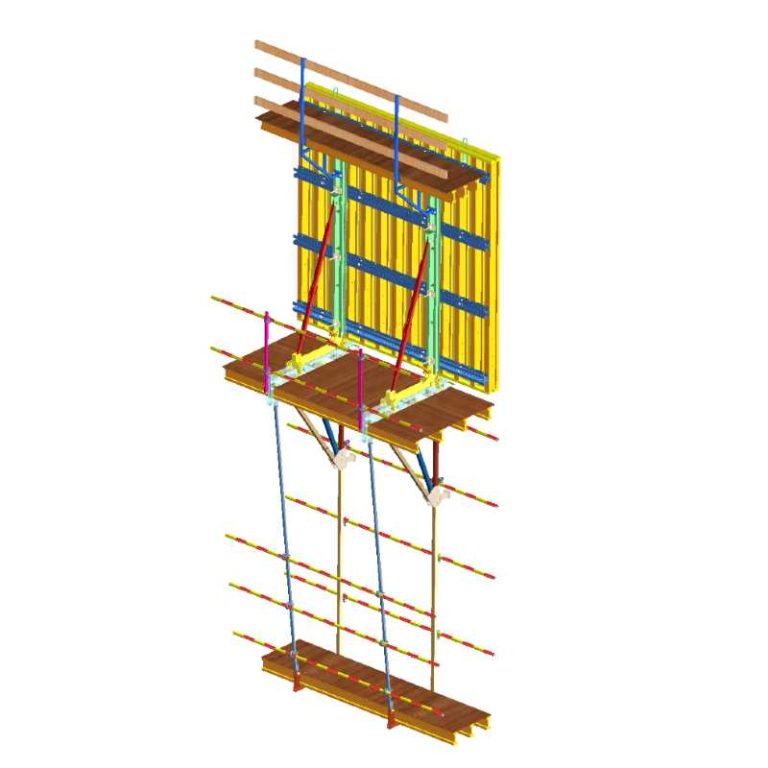
Ensuring Compatibility and Safe Integration With Aluminum Formwork in High-Rise Construction
Ensuring compatibility and safe integration with aluminum formwork in high-rise construction boosts overall system safety and workflow. GOWE Aluminium Formwork Systems match well with scaffolding to hold upright and flat builds. But they need steady checks of line-up, support spots, and weight routes. This stops uneven strain between aluminum and steel parts.
Performance Optimization: Improving Efficiency, Safety, and Lifecycle Cost
How Predictive Maintenance Reduces Total Lifecycle Cost and Enhances ROI
How predictive maintenance reduces total lifecycle cost and enhances ROI shows up in less stop time, fewer swaps, and better worker output. Predictive ways use check data, past wear paths, and ahead-of-time part swaps to stop pricey breakdowns.
Improving Worker Safety Through Inspection Discipline and Structural Monitoring
Improving worker safety through inspection discipline and structural monitoring ensures scaffold users work in managed risk spots. Firm check habits build trust that all parts, steel and aluminum both, work steadily under weight.
Increasing Reusability Cycles Across Repetitive or High-Frequency Construction Projects
Increasing reusability cycles across repetitive or high-frequency construction projects aids cost savings and resource savings. Top systems like GOWE Ringlock Scaffolding can reach longer reuse turns when cared for properly. This works best with careful tracking and cleaning.
GOWE Scaffolding Solutions: Material Advantages and Integrated Formwork Compatibility
Advantages of GOWE Steel Scaffolding Built With Q355/Q235 Materials
Advantages of Gowe steel scaffolding built with Q355/Q235 materials include better lasting power, stronger weight holding, and fighting against tiredness. We build our steel parts with frame-grade materials plus hot-dip galvanization. This backs long field use.
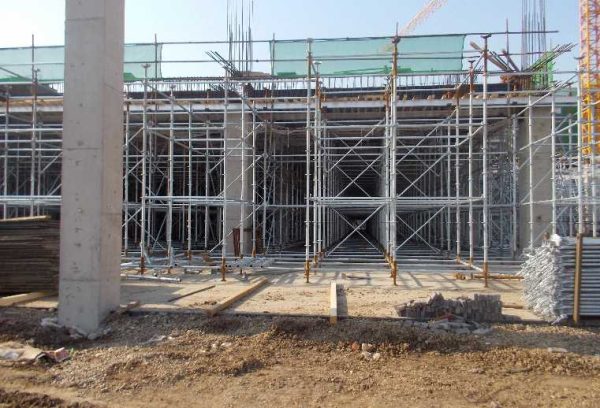

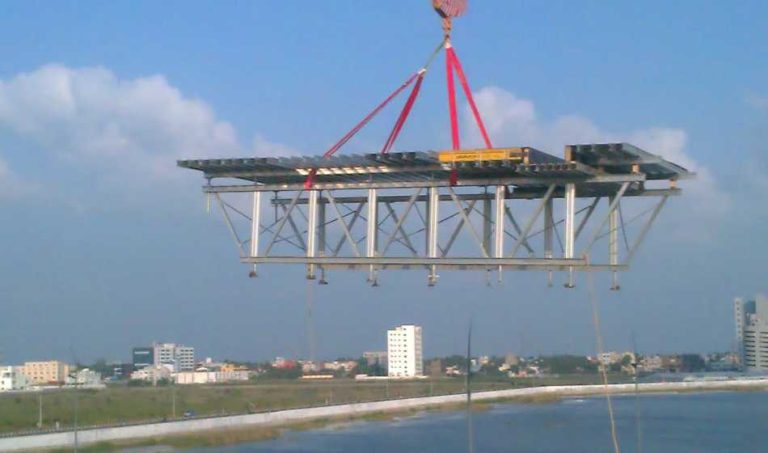
Structural Benefits of Using GOWE Aluminum Beams Together With Steel Scaffolding
Structural benefits of using GOWE aluminum beams together with steel scaffolding include better weight use, quicker setup, and stronger flat hold. Aluminum beams cut the hand-carry strain. At the same time, they keep firmness for formwork tasks.
Integration of GOWE Aluminum Formwork Systems for Efficient High-Rise Construction
Integration of GOWE aluminum formwork systems for efficient high-rise construction gives smooth workflows and less work effort. Our aluminum formwork often pairs with scaffolding to hold climb or multi-floor pour tasks.
Quality Control, Galvanization, and Production Standards That Improve Longevity
Quality control, galvanization, and production standards that improve longevity show our focus on dependability. We do raw material checks, auto welding, and weight-hold tests. This makes sure every part meets strict work needs.
FAQ: Scaffolding Maintenance, Component Care, and System Compatibility
Q: How to choose scaffolding materials that offer better long-term maintenance performance?
A: Choosing scaffolding materials with strong fatigue resistance, such as GOWE Q355 steel, helps extend system lifespan. Material stability, galvanization quality, and component compatibility should guide selection.
Q: What scaffolding system lasts longer under frequent use and heavy loads?
A: Systems like the GOWE Ringlock Scaffolding System last longer due to high-grade steel, precise welding, and hot-dip galvanization, allowing repeated use without structural compromise.
Q: How to maintain scaffolding components to reduce corrosion and structural wear?
A: Maintaining scaffolding components requires routine cleaning, protective coating application, and proper dry storage. Our galvanized components resist corrosion effectively when maintained correctly.
Q: What is the difference between steel scaffolding and aluminum beam–supported formwork in durability?
A: Steel scaffolding offers superior load capacity, while aluminum beams deliver lighter weight and easier handling. When combined, such as in GOWE hybrid support configurations, they create balanced durability and efficiency.
Q: How to ensure scaffolding compatibility with aluminum formwork in high-rise projects?
A: Ensuring compatibility requires checking support points, alignment accuracy, and load distribution. GOWE Aluminium Formwork Systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with our scaffolding for high-rise construction.