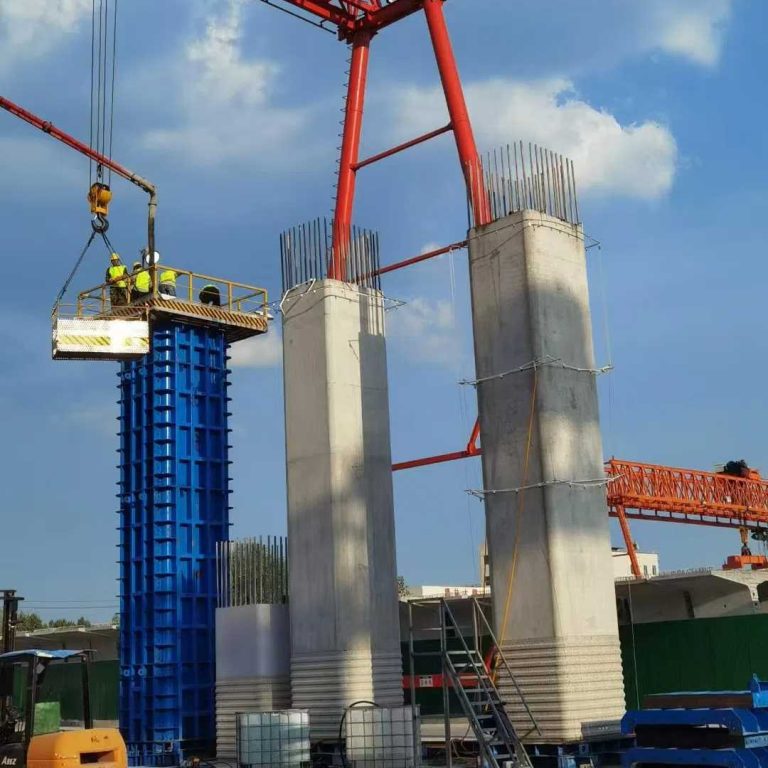
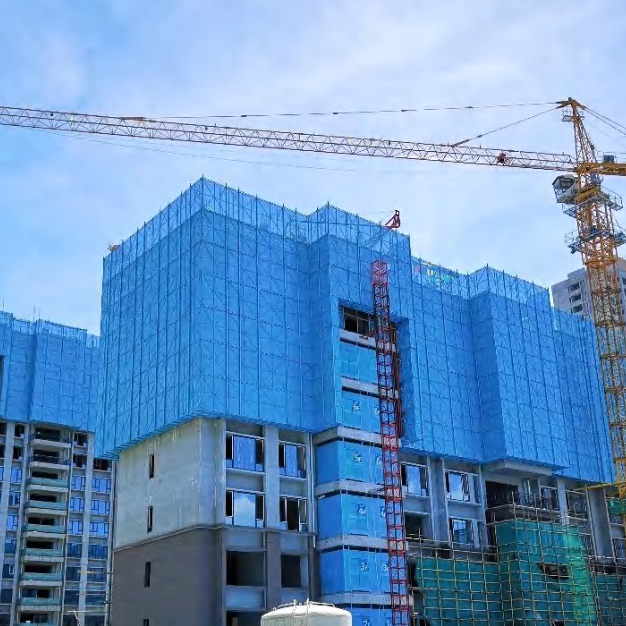
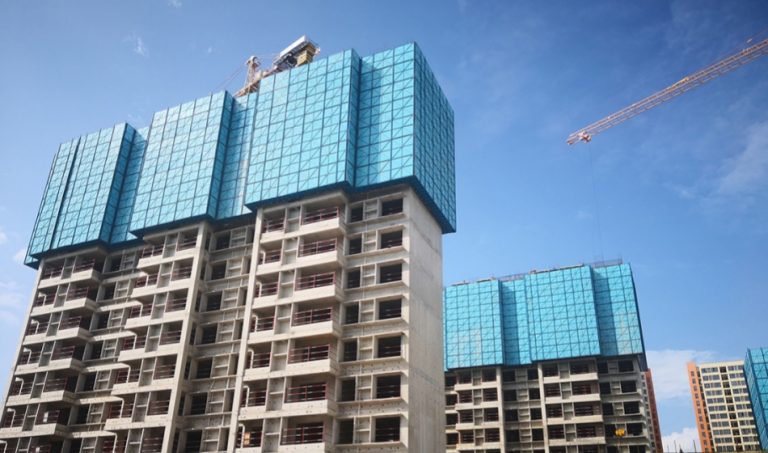
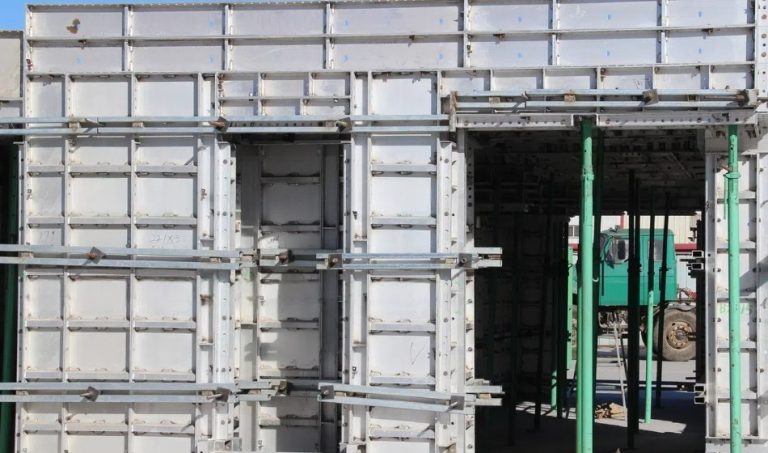
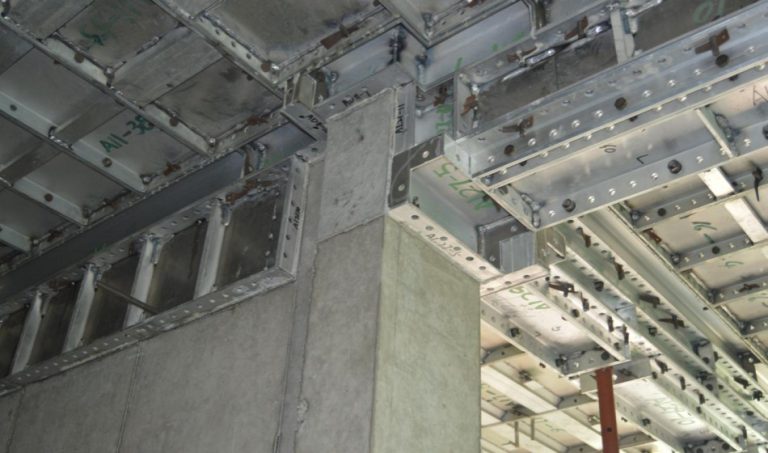
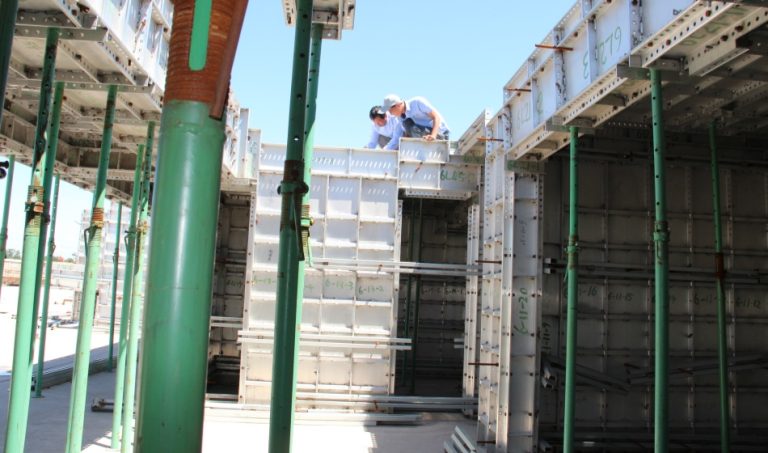
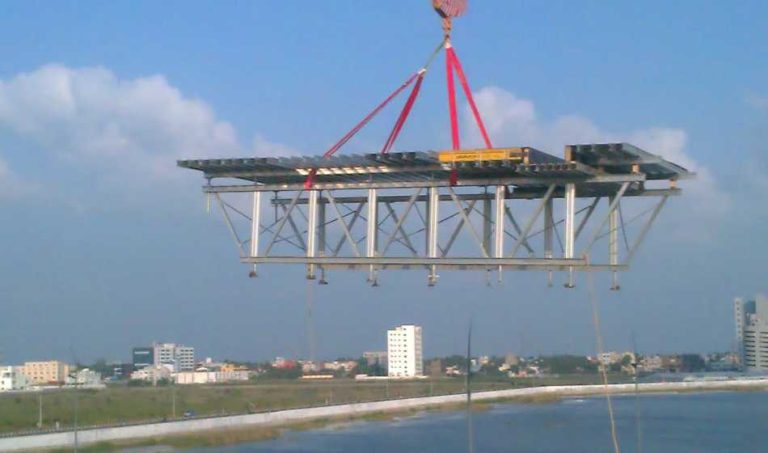
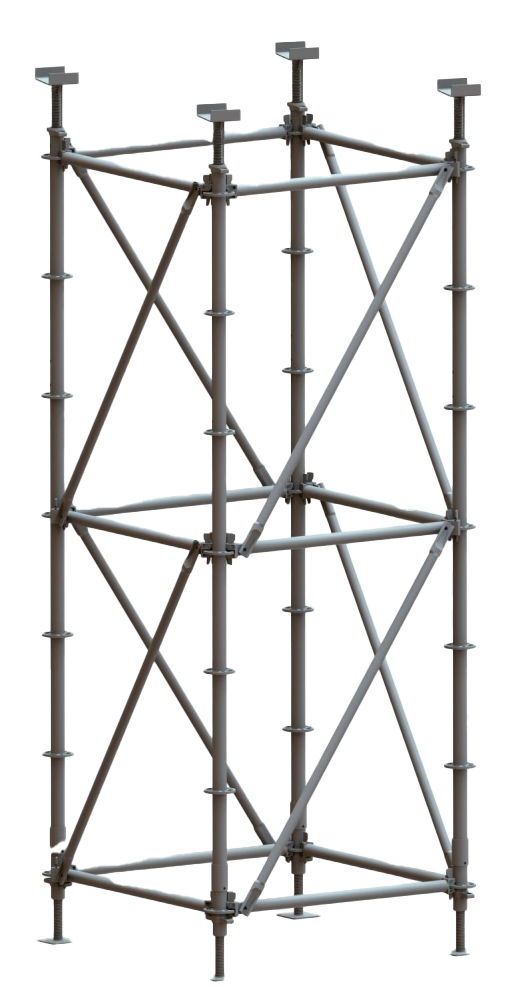
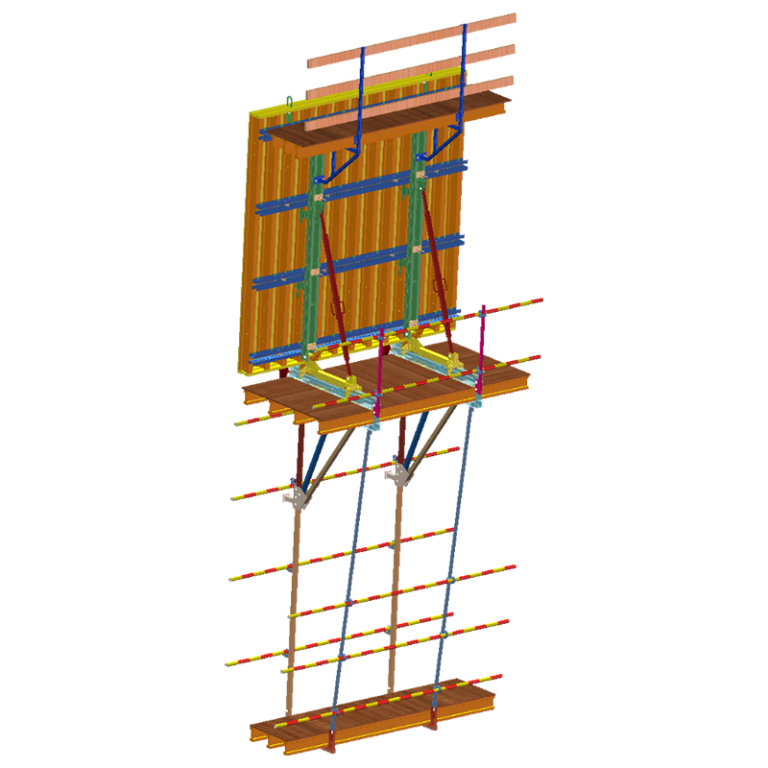
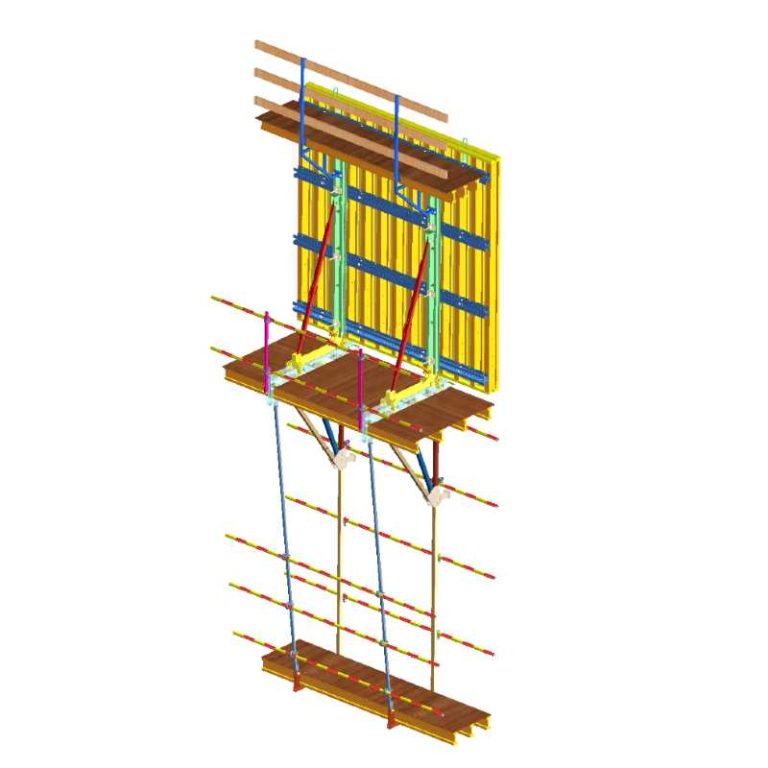
ရှေ့ခုံရဲ့ ပုံစံကို စိတ်ဝင်စားလား။ အဆောက်အအုံများကို သံမဏိ၊ အလူမီနီယံနှင့် သစ်သားကဲ့သို့သော ပစ္စည်းများဖြင့် တည်ဆောက်ထားပြီး စီမံကိန်းများ၏ အမြင့်နှင့် အရ
စက်ဖောက်တွေကို ပစ္စည်းအမျိုးမျိုးကနေ လုပ်နိုင်ပြီး တစ်ခုစီက ကိုယ်ပိုင် အကျိုးကျေးဇူးတွေရှိတယ်။ စက်ဖောင်းတွင် မကြာခဏ အသုံးပြုသော ပစ္စည်းများတွင် အောက်ပါများပါဝင်သည်။
Keluli
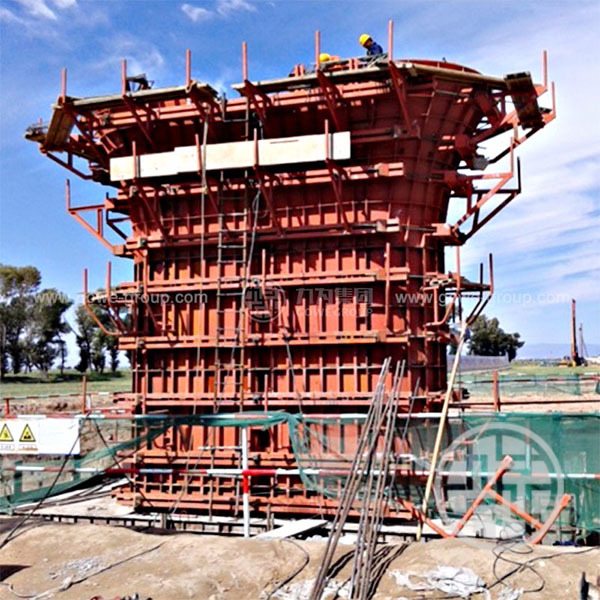
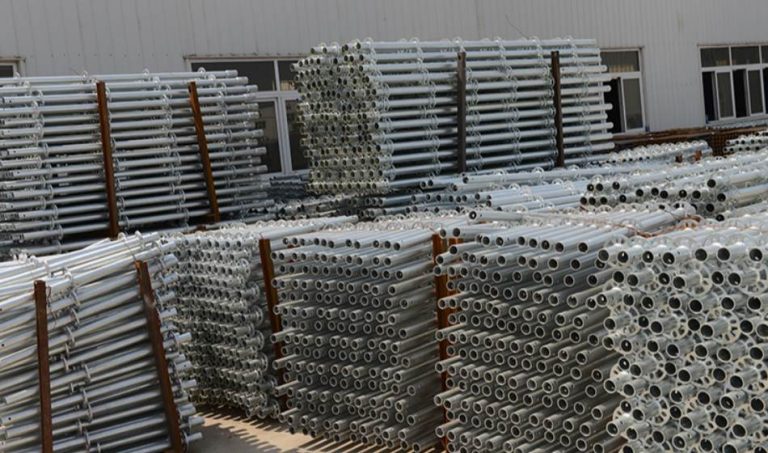
သံမဏိသည် ၎င်း၏ ခိုင်မာမှု၊ ခံနိုင်ရည်နှင့် ပြုပြင်ပြောင်းလဲနိုင်မှုကြောင့် လက်ခြေအတွက် အဓ သံမဏိခြေတပ်၏ သိသာသော လက္ခဏာများတွင် အောက်ပါများပါဝင်သည်။
- မြင့်မားသော load-bearing စွမ်းဆောင်ရည်
- ဝတ်ဆင်ခြင်းနှင့် မျက်ရည်ခံနိုင်ရည်
- ပြင်းထန်သော ရာသီဥတုအခြေအနေများနှင့် မြင့်မားသော အပူချိန်များကို ခံနိုင်စွမ်း
- အထူးသဖြင့် ချောက်ခံနိုင်ရည်အတွက် အပူရေချိုးခြင်းဖြင့် သွပ်ရည်စွမ်းထားသောအခါ
- ပုံစံနှင့် တည်ဆောက်မှုအမျိုးမျိုးနှင့် ကိုက်ညီရန် ပျော့ပျောင်းမှု
လူမီနီယမ်
အလူမီနီယမ် ရေကောင်းသည် ၎င်း၏ အလေးချိန်ပါးသော ဂုဏ်သတ္တိများကြောင့် မကြာသေးမီနှစ်များတွင် အလူမီနီယံ scaffolding ၏အကျိုးကျေးဇူးများတွင်ပါဝင်သည်:
- ကိုင်တွယ်မှု၊ သယ်ယူပို့ဆောင်ရေးနှင့် စုစည်းရေးလွယ်ကူမှု
- အဆင်ပြေသော ခိုင်မာမှု-အလေးချိန်အချိုးအစား
- ချောက်ခြင်းနှင့် အောက်ဆီဒေးခြင်းကို ခံနိုင်ရည်
- စိုစွတ်သော အခြေအနေများတွင် အသုံးပြုရန် သင့်တော်သည်
သစ်သား
ခေတ်မီဆောက်လုပ်မှုတွင် သစ်သားသည် ပိုနည်းသော်လည်း တိကျသော ရေခြံအစိတ်အပိုင်းများအတွက် အသုံးပြုနေဆဲ သစ်သား၏ အကျိုးကျေးဇူးများတွင် အောက်ပါများပါဝင်သည်။
- အတော်လေး ကုန်ကျစရိတ်ထိရောက်တဲ့ သဘာဝပစ္စည်း
- အလေးချိန်ပါးပြီး ဆောင်ရွက်နိုင်သည်
- မကြာခဏ scaffolding ပြားများနှင့်ခြေခြေပြားများအတွက်အသုံးပြုသည်
ဖန်မျှင်
မှန်အမျှင် သို့မဟုတ် မှန်အားပေးထားသော ပလပ်စတစ် (GRP) စက်ကားကို အထူးအခြေအနေများတွင် အသုံးပြုသည်။ အဓိက လက္ခဏာများတွင် အောက်ပါများပါဝင်သည်။
- လျှပ်စစ်လုပ်ငန်းများအတွက် လုံခြုံမှုအာမခံခြင်း
- မီးခံနိုင်ရည်
- ဆားရေနှင့် ပျော့ပျော့သော အက်ဆစ်မိုးရေတို့ကိုတောင် ခံနိုင်သည်။
- အတော်လေးပါး
အခြားပစ္စည်းများ
ပလပ်စတစ်: ၎င်း၏ ပျော့ပျောင်းမှု၊ မီးခံနိုင်ရည်နှင့် စိုထိုင်းခံနိုင်ရည်ကြောင့် အချို့သော ရေခြေအစိတ်အပိုင်း
ဝါး: အာရှနိုင်ငံ၏ ဒေသအမျိုးမျိုးတွင်၊ အထူးသဖြင့် ဟောင်ကောင်တွင် ရှုပ်ထွေးသော လက်ခြေတည်ဆောက်မှုများအတ
အဆောက်အအုံပစ္စည်းများကို ရွေးချယ်စဉ်တွင် စီမံကိန်းလိုအပ်ချက်များ၊ ဝန်ဆောင်စွမ်းရည်များ၊ ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေ သံမဏိသည် ၎င်း၏ စုစုပေါင်း ခိုင်မာမှုနှင့် ပုံစံမှုကြောင့် မကြာခဏ ရွေးချယ်ထားသော ပစ္စည်းဖြစ်ပြီး အလူမ မှန်ဖန်ကဲ့သို့သော အထူးပြုပစ္စည်းများကို ၎င်းတို့၏ ထူးခြားသော ဂုဏ်သတ္တိများသည် အကျိုးကျေးဇူး
အခြေခံပစ္စည်းတွေကို နားလည်ပြီးနောက် သင့်ရဲ့ တည်ဆောက်မှု လိုအပ်ချက်တွေအတွက် ဘယ်ပစ္စည်းက အကောင်းဆုံး သင့်တော်တာကို ဆုံးဖြတ်ဖို့ ကူညီပေးတဲ့ စက်
| ပစ္စည်း | ခိုင်မာမှု | အလေးချိန် | ခံနိုင်ရည် | ချောက်ခံနိုင်ရည် | အကောင်းဆုံးအတွက် |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keluli | အလွန်မြင့် | လေးထန် | အလွန်မြင့် | မြင့်မားသော (galvanized လျှင်) | ရေရှည်၊ အမြင့်၊ စက်မှုလုပ်ငန်း |
| လူမီနီယမ် | အလတ်အလတ် | အလင်း | အလတ်အလတ် | မြင့်မားသော | ထိန်းသိမ်းမှု၊ မိုဘိုင်း setup များ |
| သစ်သား | နိမ့်မှ အလတ်အလတ် | အလင်း | နိမ့် | နိမ့် | အသေးစား၊ ယာယီပလက်ဖောင်းများ |
| ဖန်မျှင် | အလတ်အလတ် | အလင်း | မြင့်မားသော | အလွန်မြင့် | လျှပ်စစ်၊ ဓာတုပတ်ဝန်းကျင်များ |
| ဝါး | အလတ်အလတ် | အလင်း | အလတ်အလတ် | အလတ်အလတ် | အာရှရှိ အစဉ်အလာ တည်ဆောက်မှုများ |
စက်ဖော်အတွက် စံပစ္စည်းက ဘာလဲ။
ရေခြေအတွက် ပုံမှန် ပစ္စည်းကို သိလိုပါသလား။ Keluli ၎င်း၏ ခံနိုင်ရည်၊ ခိုင်မာမှုနှင့် ဝန်ဆောင်စွမ်းရည်ကြောင့် အများဆုံး အသုံးပြုသော ပစ္စည်းဖြစ်ပြီး အမြင့်ဆုံး လုံ
သံမဏိဟာ ရေရှည်ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး စီမံကိန်းတွေအတွက် ပြီးပြည့်စုံတဲ့ ခံနိုင်ရည်နဲ့ ခိုင်မာမှုကြောင့် ရေရှည် ၎င်းသည် ပြင်းထန်သော ရာသီဥတုအခြေအနေများအား ခံနိုင်ရပြီး တည်ငြိမ်ပြီး ဘေးကင်းသော အလုပ်ပလက်ဖောင်းကို
ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် စက်ဖောက်အတွက် စံပစ္စည်းက သံမဏိပါ။ သံမဏ ၎င်းသည် ရာသီဥတုနှင့် ဝတ်ဆင်မှုကို ခံနိုင်ရပြီး ကာလရှည်အတွင်း စက်ဖော်တည်ဆောက်မှုများကို တည်ငြိမ် သံမဏိကို မကြာခဏ ချောက်မှုကနေ ကာကွယ်ရန် အသုံးပြုပြီး ပြင်ပပပတ်ဝန်းကျင်တွေမှာ လက်ခြေရဲ့ သက်တမ်းကို သံမဏိခြေတွေဟာ အလူမီနီယံလို အခြားနည်းတွေထက် ပိုလေးပေမဲ့ ခိုင်မာမှုက အမြင့်ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး၊ စက်မှုစီမံကိန်းကြီးတွေနဲ့ ရေရှည်ခြ
အများဆုံး အသုံးပြုထားသော ရေခုံအမျိုးအစားက ဘာလဲ။
ခင်ဗျားဟာ အများဆုံး ပျံ့နှံ့မှုရှိတဲ့ ရေခုံအမျိုးအစားကို ရှာနေလား။ ပြွန်နှင့် ချိတ်ဆက်စက်စက်ကို ဆောက်လုပ်ရေးလုပ်ငန်းတွင် ကျယ်ပြန့်စွာ အသုံးပြုပြီး ၎င်း၏ ပြုပြင်နိုင်မှုကြောင့် ဆောက်လုပ်
အများဆုံး မကြာခဏ အသုံးပြုသော စက်ဖော်အမျိုးအစားသည် ပြွန်နှင့် ချိတ်ဆက်စက်ဖော်ဖော်ဖြစ်ပြီး သိသာသော ပျော့ပျောင်းမှုကို ပေးပြီး ပုံစ ၎င်းကို တည်ဆောက်မှုတွင် ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် အသုံးပြုသည် ၎င်း၏ ရိုးရှင်းသော စုစည်းမှုနှင့် သိသာသော ဝ
အကျယ်ပြန့်စွာအသုံးပြုသော scaffolding အမျိုးအစား ပြွန်နှင့် coupler ကြိုးဤစနစ်သည်သံမဏိပြွန်များနှင့် couplers များကိုအသုံးပြုပြီး versatile နှင့်ညှိနိုင်သောဘောင်ကိုဖွဲ့စည်းသည်။ ၎င်း၏လူကြိုက်များမှုသည် ၎င်း၏ပျော့ ပြွန်နှင့် ချိတ်ဆက်စက်စက်သည် လေးထန်သော ဝန်ဆောင်မှုများကို ထောက်ပံ့နိုင်ပြီး ကြီးမားသော ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး အခြားပျံ့နှံ့သော အမျိုးအစားများတွင် တည်ဆောက်ရန် ပိုရိုးရှင်းပြီး အခြေခံဆောက်လုပ်ရေးလုပ်ဆောင်ချက်များအတွက် အသုံးပြုသော ဘောင်မြေတပ်
အလူမီနီယမ် ရေကောင်းကို ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး လုပ်ငန်းမှာ လူကြိုက်များတဲ့ ရွေးချယ်မှုတစ်ခုအဖြစ်
သင်ဟာ ပေါ့ပါးတဲ့ ရေခြေဖြေရှင်းနည်းကို ရှာနေရင် အလူမီနီယမ် scaffolding မကြာခဏ ၎င်း၏ သယ်ဆောင်နိုင်မှု၊ ရိုးရှင်းသော စုစည်းမှုနှင့် အညက်ခံနိုင်မှုအတွက် ရွေးချယ်ထားပြီး ၎င်းသည် မကြာခဏ
အလူမီနီယမ် ရေကောင်းသည် ၎င်း၏ ပေါ့ပါးသော တည်ဆောက်မှု၊ လွယ်ကူသော တည်ဆောက်မှုနှင့် အနှောက်ခံနိုင် ၎င်းရဲ့ သယ်ဆောင်နိုင်မှုက ပုံမှန် ပြင်ဆင်မှု (သို့) လှုပ်ရှားမှု လိုအပ်တဲ့ စီမံကိန်းတွေအတွက သို့သော်လည်း အလူမီနီယမ်သည် သံမဏိရဲ့ ခိုင်မာမှုမရှိပြီး ကြီးမားပြီး အလေးအထန် ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး အားထုတ်မှုများတွင် ၎
အလူမီနီယမ် ရေကောင်း၏ လူကြိုက်များမှုသည် ၎င်း၏ အလေးချိန်ပါးသော လက္ခဏာများကြောင့် ဖြစ်နိုင်ပြီး လွယ်ကူစွာ သယ်ယူပို့ဆော ၎င်းသည် ပန်းချီခြင်း၊ ပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းရေး သို့မဟုတ် ပြုပြင်ရေးလုပ်ငန်းများအတွင်းကဲ့သို့သော မကြာခဏရွှေ့ပြောင်းရမည့် စီမံကိန ချောက်ခံနိုင်ရည်သည် ပြင်ပအသုံးပြုမှုများအတွက် သို့မဟုတ် စိုထိုင်းသို့မဟုတ် ဓာတုပစ္စည်းများ ရှိသည့် နေရ သို့သော်လည်း အလူမီနီယမ်သည် သံမဏိနှင့် တူညီသော ခိုင်မာမှု သို့မဟုတ် ဝန်ဆောင်မှုစွမ်းဆောင်ရည်ကို မထောက်ပံ့ပေးပြီး အလေး ဒီအားနည်းချက်ပေမဲ့ အလူမီနီယံ ရေခုံဟာ ၎င်းရဲ့ အဆင်ပြေမှု၊ စွမ်းဆောင်ရည်နဲ့ သယ်ဆောင်နိုင်မှုကြောင့် အကြိုက်ဆ
၎င်း၏ အကျိုးကျေးဇူးများနှင့် ဆန့်ကျင်မှုများ သံမဏိ Scaffolding?
အမြင့်ဆုံး ခိုင်မာမှု လိုအပ်ရင် သံမဏိရေခြေဟာ ခိုင်မာပြီး ခိုင်မာပြီး အလေးထန်တဲ့ စီမံကိန်းတွေအတွက် သင့် သို့သော်လည်း ၎င်း၏ အလေးချိန်သည် သယ်ဆောင်နိုင်မှုနှင့် စုစည်းမှုလွယ်ကူမှုနှင့် ပတ်သက်၍
သံမဏိ scaffolding ထူးခြားတဲ့ ခိုင်မာမှုနဲ့ ခံနိုင်ရည်ကို ပေးပြီး ကျယ်ပြန့်တဲ့ ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး ကြိုးပမ်းမှုတွေအတွက် စံပြ သို့သော်လည်း ၎င်း၏ အလေးချိန်သည် ပို့ဆောင်ခြင်းနှင့် စုစည်းခြင်းသည် ပိုခက်ခဲသောကြောင့် အလုပ်သမားကုန်ကျစရိတ်နှင့် အချ ဒါပေမဲ့ တည်ငြိမ်မှုဟာ တောင်းဆိုတဲ့ တာဝန်တွေအတွက် စိတ်ချရဆုံး ရွေးချယ်မှုအဖြစ် တည်နေပါတယ်။
သံမဏိစက်ကားဟာ ၎င်းရဲ့ ခိုင်မာမှုမြင့်မားတဲ့ စွမ်းဆောင်ရည်နဲ့ ဝန်ကို သက်ဆောင်နိုင်စွမ်းကဲ့သို့တဲ့ အကျိုးကျေးဇူးများစွာ ၎င်းသည် ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိပြီး ပြင်းထန်သော ရာသီဥတုအခြေအနေများကို ခံနိုင်ပြီး အလုပ်သမားများ၏ ဘေးကင်း သို့သော်လည်း သံမဏိရှိ အဓိကအားနည်းချက်က ၎င်း၏ အလေးချိန်ဖြစ်ပြီး ၎င်းသည် အခြားနည်းပစ္စည်းများထက် ပိုလေးပြီး သယ်ယူပို့ သံမဏိခြေတည်ဆောက်ရန် လိုအပ်သော ထပ်ဆောင်းလုပ်ငန်းသည် ကုန်ကျစရိတ်များ ပိုမြင့်မားပြီး စီမံကိန်းအချိန ဤအားနည်းချက်များသော်လည်း သံမဏိသည် ၎င်း၏ စိတ်ချရမှုနှင့် သက်တမ်းရှည်မှုကြောင့် အထူးသဖြင့် အမြင့်ဆုံး တည်ငြိမ်မှုနှင့်
အခြားပစ္စည်းများကို စက်ဖောင်းတွင် အသုံးပြုပါသလား။
ရှေ့ခြေအတွက် အခြားပစ္စည်းတွေကို စိတ်ဝင်စားလား။ သံမဏိ၊ အလူမီနီယံနှင့် သစ်သားအပြင် ဝါးနှင့် မှန်ဖယ်ကဲ့သို့သော အခြားပစ္စည်းများကို ၎င်းတို့၏ ထူးခြားသော အကျိုး
သံမဏိ၊ အလူမီနီယံနှင့် သစ်သားတို့သည် လက်ခြေအတွက် အဓိကပစ္စည်းများဖြစ်သော်လည်း ဝါးကို တရုတ်နှင့် အိန္ဒိယကဲ့သို့သော ဖန်မျှင်အမျှင်စက်ဖောင်းသည် လျှပ်စစ်အလုပ်များ သို့မဟုတ် ချောက်ခံနိုင်မှုအရေးကြီးသော ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်များအတွက် သင့်တော်သ
သံမဏိ၊ အလူမီနီယံနှင့် သစ်သားများ၏ ပုံမှန်အသုံးပြုသော ပစ္စည်းများအပြင် ဒေသများနှင့် စက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းအမျိုးမျိုးတွင် ဝါး scaffolding တရုတ်နဲ့ အိန္ဒိယလို နိုင်ငံတွေမှာ ပျံ့နှံ့ပြီး အထူးသဖြင့် ဟောင်ကောင်လို မြို့တွေမှာ သမိုင်းရှည်ရှိပါတယ်။ ဝါးဟာ အလေးချိန်ပါးပြီး ပျော့ပျော်နိုင်ပေမဲ့ အံ့သြစရာ အားကောင်းပြီး လူဦးရေပြည့်စုံတဲ့ ဒေသတွေမှာ လျင်မ နောက်တစ်ခုက မှန်ဖန် scaffoldingလျှပ်စစ်အလုပ်လုပ်ခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် ရေအနီးသို့မဟုတ် ဓာတုစက်ရုံများကဲ့သို့သော ချောက်ခံနိုင်ရည်မရှိမရှိသော နေရာ ဒီပစ္စည်းတွေကို မကြာခဏ အသုံးပြုပေမဲ့ တိကျတဲ့ စီမံကိန်းနဲ့ နေရာကို မူတည်ပြီး ထူးခြားတဲ့ အကျိုးကျေးဇ
Kesimpulan
အနှစ်ချုပ်အားဖြင့် စီမံကိန်း၏ အရွယ်အစား၊ တည်နေရာနှင့် တိကျသော လိုအပ်ချက်များကြောင့် စက်ဖော်ပစ္စည အများဆုံး အသုံးပြုသော ပစ္စည်းများတွင် သံမဏိ၊ အလူမီနီယံနှင့် သစ်သားများ ပါဝင်ပြီး ဝါးနှင့် မှန်ဖန်သည် ပျော့ပျောင်းမှု သို့မဟုတ်