The following are the main safety requirements for using scaffolding in accordance with OSHA regulations, based on the search results:
Capacity for Fall Protection and Electrical Hazards in Construction
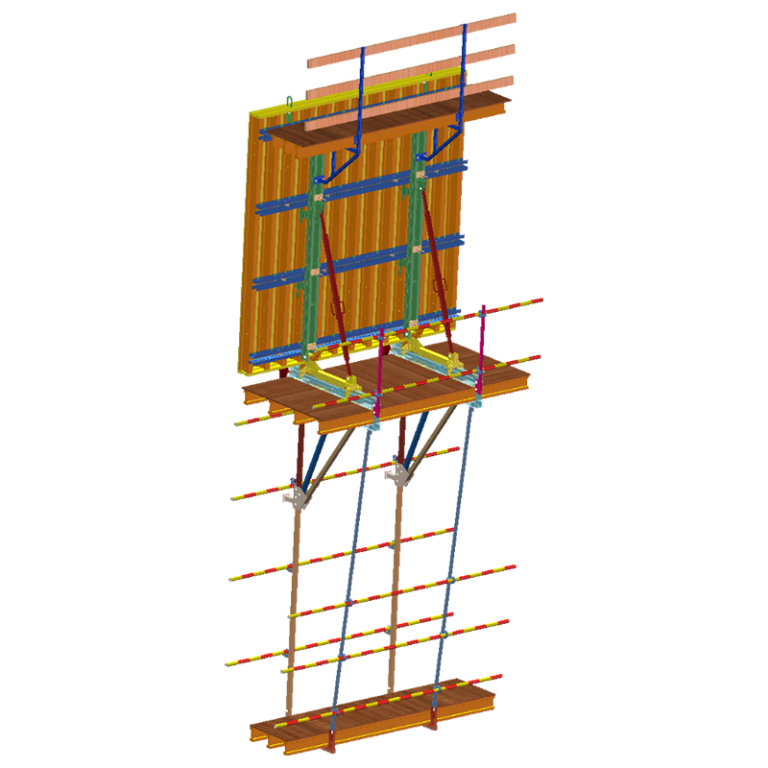
Fall protection guardrails, personal fall arrest devices, or both must be used to prevent falls for workers on scaffolds higher than ten feet above a lower level.
Midrails should be positioned roughly midway between the toprail and the platform surface, and guardrails should be installed between 38 and 45 inches high.
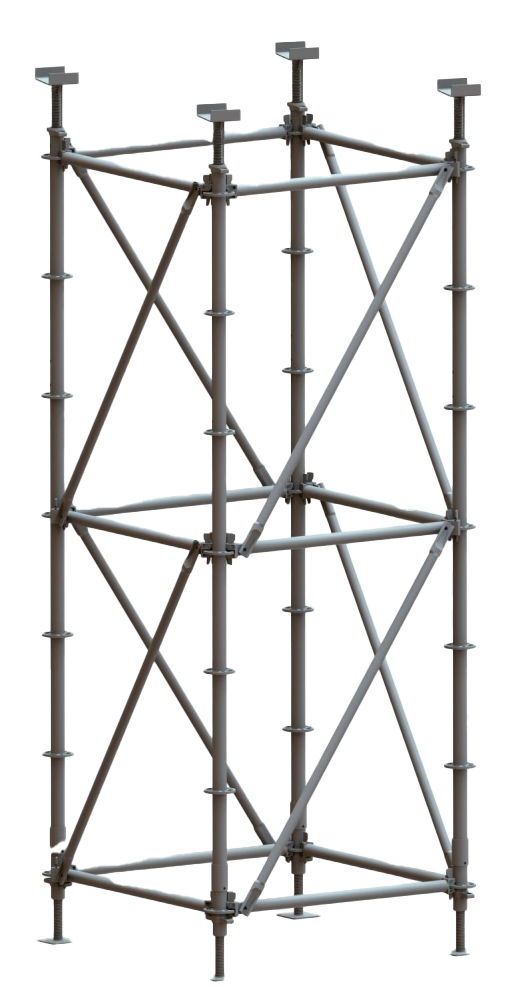
Construction and Capacity Scaffolds and scaffold parts must be able to sustain at least four times the maximum intended load without failing. ItIt is essential to use high-quality equipment from reputable scaffolding manufacturers, such as Gowe Scaffolding, to ensure compliance with these safety standards.
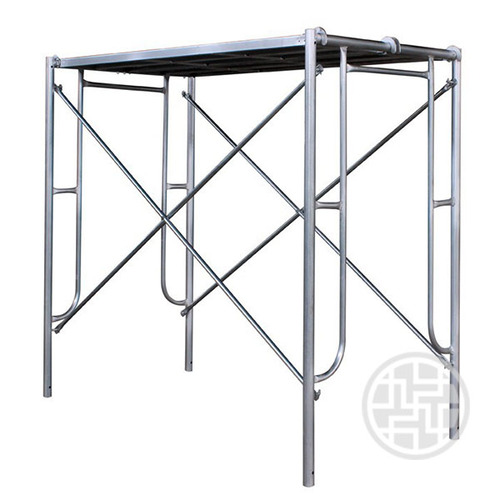
In addition to having appropriate guardrails, midrails, and toeboards along open sides, scaffold platforms ought to be completely planked or decked.
Level, sturdy footings that can hold up the weighted scaffold are essential.
Installing guying ties and braces should be done in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions or whenever the height-to-base ratio is greater than 4:1.
Electrical Risks
Scaffolds and electrical hazards should be at least ten feet apart. The line’s power must be cut off if a shorter distance is needed.
Examining and maintaining
Before every work shift and after any incident that might compromise the scaffolding’s structural integrity, a qualified individual must visually inspect the scaffolding.
It is crucial to perform routine maintenance, which includes cleaning after every task and checking for damaged or broken parts.
Training: Every employee engaged in scaffolding work must receive training from their employers, which must cover subjects like
- Using scaffolds and materials appropriately
- Identifying and reducing risks
- Maximum intended load and carrying capacity
- Extra Safety Procedures
- Wear the appropriate PPE, such as non-slip shoes and hard hats.
- To avoid trips and falls, keep work areas neat and clutter-free.
- Put up barriers to prevent cars and large machinery from accessing the scaffold base.
- When climbing scaffolds, keep three points of contact.
Employers can guarantee OSHA compliance and drastically lower the risk of scaffold-related injuries by following these safety guidelines.
Following load capacity limits, making sure scaffolding is assembled and disassembled correctly, utilizing fall protection devices like guardrails, and performing daily inspections are all part of scaffolding safety regulations. These precautions reduce the possibility of mishaps and guarantee that scaffolding is always sturdy and safe for workers.
After learning the fundamentals of safety, let’s examine the particular rules and specifications established by OSHA and ISO to guarantee scaffolding is secure and safe for construction workers.

OSHA’s Scaffolding Safety Standards: What Are They?
Are you wondering what OSHA requires? OSHA’s scaffolding safety regulations address fall protection, load capacity, and required inspections to guarantee worker safety when performing maintenance or construction work on raised platforms.
According to OSHA’s scaffolding safety standards, scaffolding must be able to support four times its intended load in addition to its weight, have guardrails to prevent falls, and be inspected every day. These rules are intended to keep scaffolding safe for workers and to prevent mishaps.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, has comprehensive regulations that are essential for scaffolding safety. These include the requirement that scaffolding bear four times the maximum load that is intended and its own weight. Fall protection features like guardrails, midrails, and toeboards are necessary for scaffolding that is higher than ten feet. Before every shift, scaffolding must also be examined by a qualified individual to look for potential dangers like loose parts or damage. Decking and planking need to be tight and free of any openings that might trip employees. To guarantee safety at every stage of use, OSHA also requires that scaffolding be correctly erected and dismantled by trained personnel.
What General Safety Standards Apply to Scaffolding?
Are you worried about safety in general? To reduce the risk of accidents, scaffolding needs to meet a number of requirements, such as load-bearing capacity, appropriate access, and sufficient fall protection systems.
Load-bearing capacity, appropriate access points (such as ladders), and the use of fall protection devices like guardrails and harnesses are all general scaffolding safety requirements. Maintaining worker safety and averting mishaps on building sites requires that the scaffolding be level, sturdy, and routinely inspected.
Scaffolding general safety regulations address a number of important topics. First and foremost, scaffolding needs to be able to support at least four times the maximum load that is intended in addition to its own weight. For safe entry and exit, access points like stairways and ladders need to be installed correctly. Scaffolding over ten feet must have fall protection devices, such as guardrails, midrails, and safety harnesses. To avoid tipping or shifting, the structure should have firm foundations and be level and stable. In order to keep workers from slipping or falling through gaps, scaffolding needs to be inspected on a regular basis and the platforms need to be completely planked. To avoid injuries, proper scaffold assembly, disassembly, and use training is crucial.
What Are the Scaffolding Fall Protection Requirements?
Fearful of falling? To prevent workers from falling from heights, scaffolding must have fall protection systems, such as guardrails, toeboards, and harnesses.
Guardrails, midrails, and toeboards are all used in scaffolding fall protection to keep workers from falling. These safeguards need to be put in place for scaffolding that is higher than ten feet. For added safety, personal fall arrest devices, such as harnesses, might also be necessary.
One of the most important prerequisites for scaffolding safety is fall protection. In order to prevent workers from falling, OSHA mandates that scaffolding platforms that are more than ten feet above the lower level have guardrails, midrails, and toeboards. Midrails must be positioned halfway between the guardrail and the platform, and guardrails must be between 38 and 45 inches high. Depending on the project and local laws, employees may also be obliged to wear personal fall arrest devices, like safety harnesses. These systems aid in preventing workers from falling to the ground in the event of a slip. To guarantee worker safety, all fall protection equipment must be installed correctly and inspected on a regular basis.
What Is the Scaffolding Minimum Safety Factor?
Are you curious about safety factors? For scaffolding to guarantee worker safety, it must be designed with a safety factor of at least four, which means it must sustain four times the anticipated load.
Scaffolding must have a safety factor at least four times the intended load. In order to ensure that scaffolding can withstand unforeseen stresses or weight increases during construction without collapsing or becoming unstable, it must support four times the maximum load it will carry.
Four times the intended load is the minimum safety factor for scaffolding. Scaffolding must therefore be constructed and designed to support a minimum of four times the maximum load that it is anticipated to support during regular use. This safety factor is essential because it takes into consideration the possibility of load increases brought on by unforeseen additions to the scaffolding, such as additional personnel, supplies, or equipment. The safety factor lowers the chance of scaffolding failure or collapse during construction activities by ensuring that it stays secure and stable even under increased stress.
What Safety Standards Apply to the Construction and Disassembly of Scaffolding?
Concerned about setting up scaffolding? To guarantee worker safety and avoid mishaps, scaffolding erecting and dismantling safety requirements include appropriate training, fall protection, and supervision.
The use of trained personnel, the installation of fall protection equipment, and the guarantee of competent supervision are all necessary for the safe erection and dismantling of scaffolding. To ensure safety during setup and takedown, the right procedures must be followed to avoid collapse or instability.
Strict safety protocols must be followed when erecting and dismantling scaffolding to guarantee the structure’s stability. To guarantee that scaffolding components are put together correctly, workers engaged in setup and takedown must receive the necessary training and be closely monitored by a qualified individual. To prevent falls, fall protection equipment, like guardrails or safety harnesses, must be installed during setup. To avoid tipping or collapsing, it is also crucial to make sure the scaffolding is constructed on a level, stable surface. Accidents during scaffolding assembly and disassembly can be avoided by following the right procedures and making sure that all parts are firmly fastened.
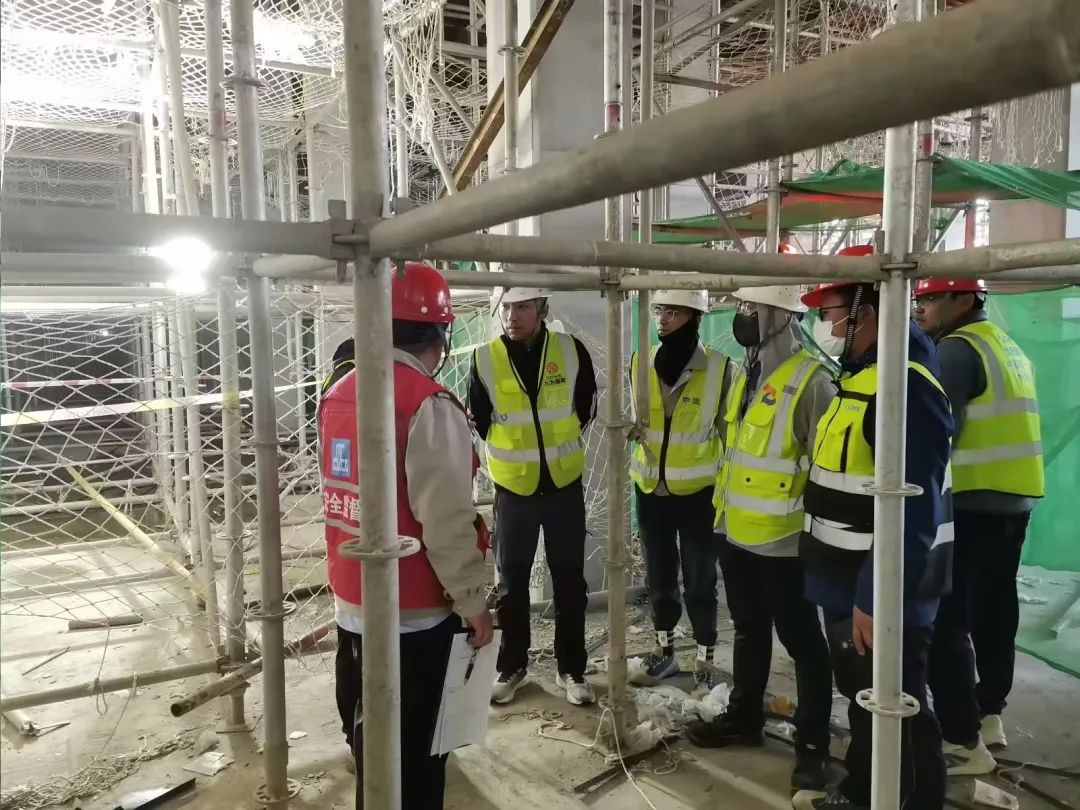

What Kind of Training Is Needed for Employees Using Scaffolding?
Do you have questions about training? In order to reduce accidents, workers who use scaffolding must receive training to make sure they know how to assemble, use, and disassemble scaffolding safely.
To avoid mishaps, workers must receive training on how to assemble, use, and disassemble scaffolding correctly. This entails being aware of possible risks, comprehending load capacities, and using fall protection devices. Retraining should be done on a regular basis to make sure employees continue to follow safety procedures.
To guarantee that they know how to safely assemble, operate, and disassemble scaffolding systems, workers must complete specialized training. Topics covered in training include how to identify and reduce possible hazards, how much weight scaffolding can support, and how to use fall protection equipment correctly. Emergency protocols, such as how to handle mishaps or equipment malfunctions, should also be taught to employees. To guarantee that employees continue to adhere to the most recent safety standards and are informed of any modifications to safety rules or equipment, regular retraining is required.
In conclusion
To sum up, the main goals of scaffolding safety regulations are to guarantee that structures are sturdy, correctly put together, and have fall protection. Maintaining a safe working environment on scaffolding requires regular inspections, appropriate training, and adherence to OSHA and ISO standards.