Introduction
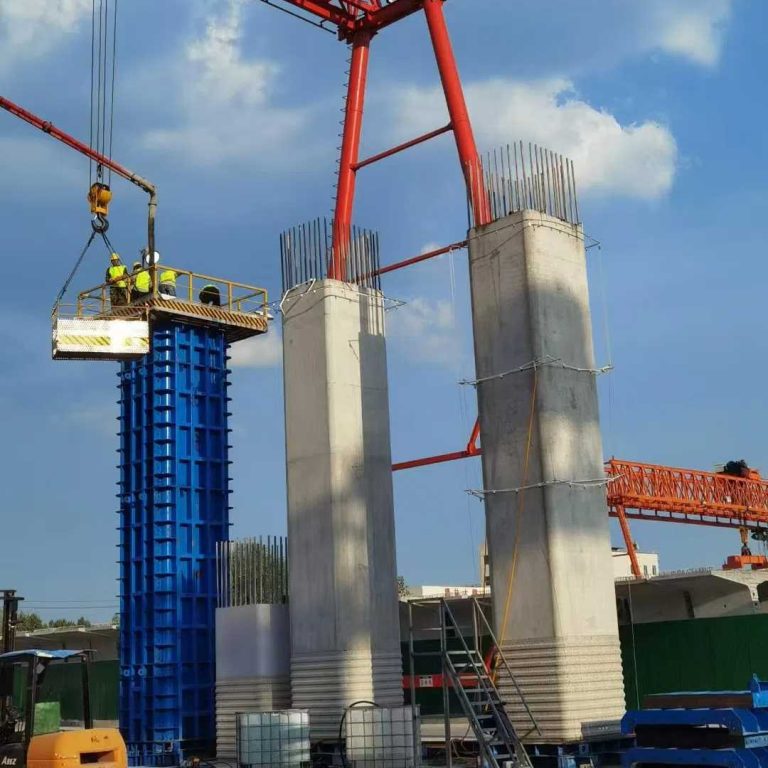
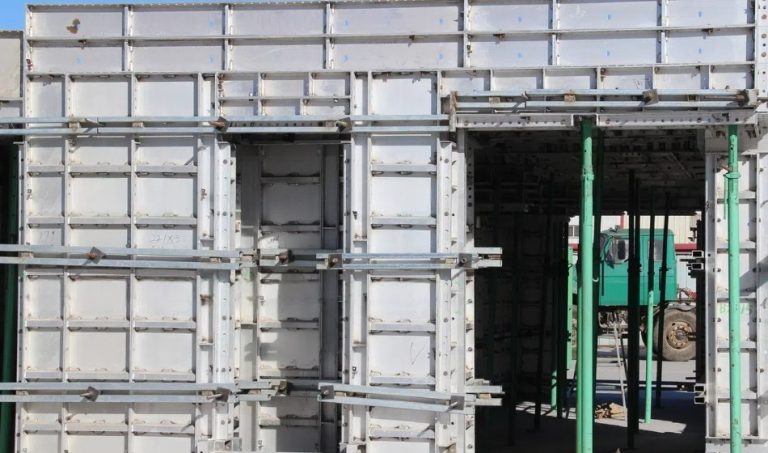
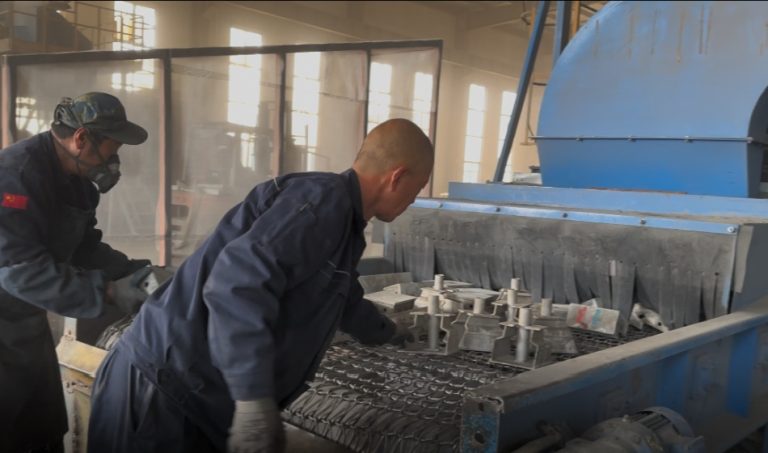
Formwork is one of the most important parts of a construction project nowadays since it affects the quality, cost, and pace of the work. Formwork is like a mold that shapes concrete into walls, slabs, beams, and columns.
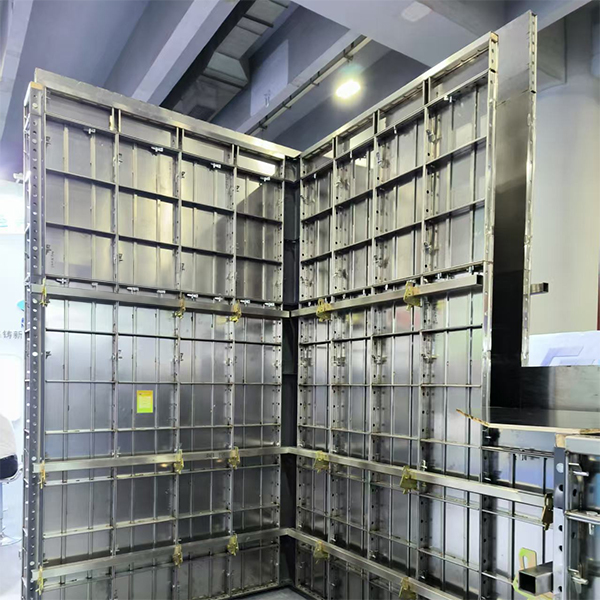
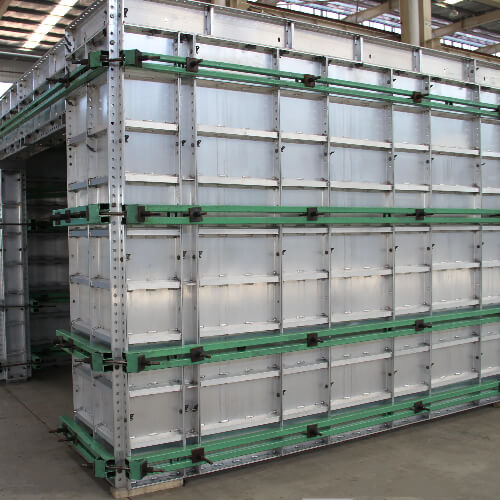
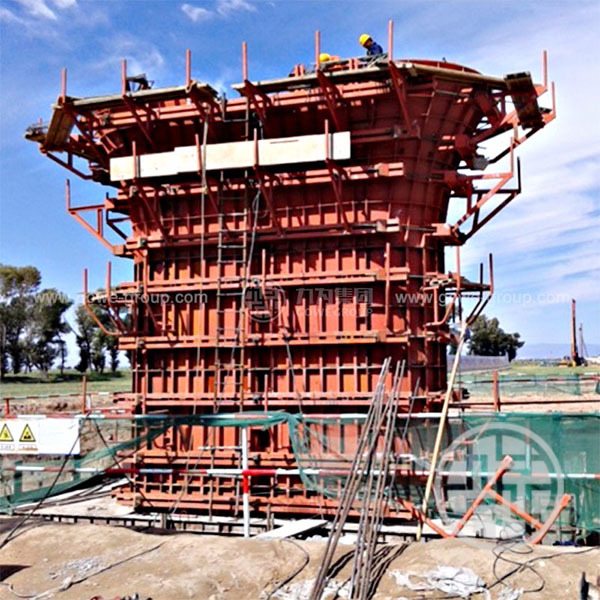
Aluminum formwork has become a popular choice in the previous few decades, even if there are many other materials to choose from, such as wood, plywood, steel, and plastic. Developers and contractors both prefer it since it is light, can be used again, and can build flawless concrete finishes.
Aluminum formwork has some major drawbacks, too, even though it has certain benefits. This material isn’t always the greatest choice because it might be expensive up front and has structural problems. This in-depth study will look at the problems with aluminum formwork, compare it to other materials, and answer some of the most common queries about using it.
For a deeper insight into professional formwork solutions, you can also check resources from GOWE Formwork Systems, a trusted name in innovative construction technologies.
What are two problems with using aluminum?
Aluminum formwork is very common; however, it has two big problems that often make builders not want to utilize it:
A lot of money up front
Aluminum formwork systems are far more expensive than wood or plywood. They may be used over and over again, but the high cost makes them unsuitable for small contractors or projects that only need them once.
Not very flexible on site.
Aluminum panels are made to order in particular sizes. Once they are made, it is not easy to cut, alter, or change them on the job site. If the design changes, the contractor might have to buy new panels, which will take more time and money.
For contractors seeking alternatives, GOWE customized formwork solutions provide a balance between cost and efficiency.
Why don’t builders always use aluminum?
Aluminum formwork works well for structures that are built over and over again, like housing projects, however there are a few reasons why it isn’t usually used:
Structural Limitations: Aluminum can’t hold as much weight as steel, so it can’t be used for tall towers or huge industrial buildings.
Corrosion Concerns: In very alkaline concrete conditions, the natural oxide layer that protects aluminum can break down, which might cause problems with long-term durability.
Require for Skilled Labor: Workers require particular training to put together and take care of aluminum formwork effectively, which raises the cost of labor.
Fire Safety Risks: Aluminum loses strength quickly when it becomes really hot, which can make buildings more dangerous in places that are prone to fires.
Many construction companies prefer to combine aluminum and steel systems to offset these weaknesses. Providers like GOWE specialize in hybrid solutions, ensuring both safety and cost-effectiveness.

What are two bad things about aluminum?
From a materials science point of view, aluminum has two major problems:
Not as strong as steel – Aluminum is light, yet it can’t handle tremendous loads and strains like steel can.
Corrosion in Harsh Environments-Aluminum doesn’t rust easily, but it can be damaged in places with high levels of alkaline and chloride, such marine construction. This can shorten its life.
What is the best material to use for formwork?
The appropriate formwork material will depend on the project’s aims, price, and how long it needs to last. Here’s a short look at the differences:
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use Case |
| Timber/Plywood | Cheap, flexible, easy to cut and modify | Short lifespan, warps easily | Small-scale or one-time projects |
| Steel | Strong, durable, highly reusable | Heavy, expensive to transport | High-rise, industrial, long-term projects |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, quick to assemble, reusable | Expensive, less flexible | Repetitive housing and mid-rise structures |
| Plastic/Composite | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, eco-friendly | Expensive, limited load capacity | Green and modular construction |
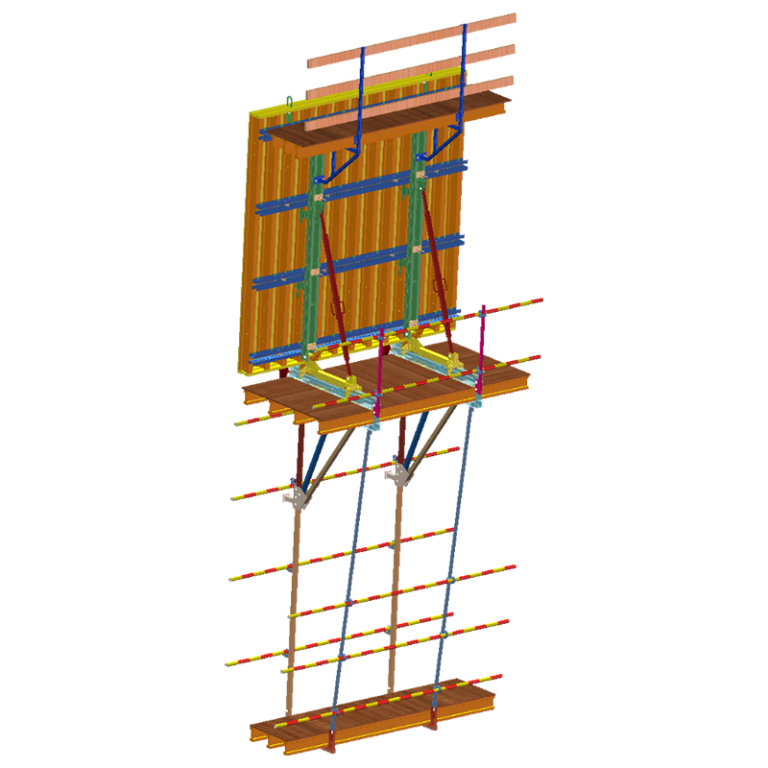
What kinds of aluminum formwork are there?
There are several different types of aluminum formwork systems, each with its own use:
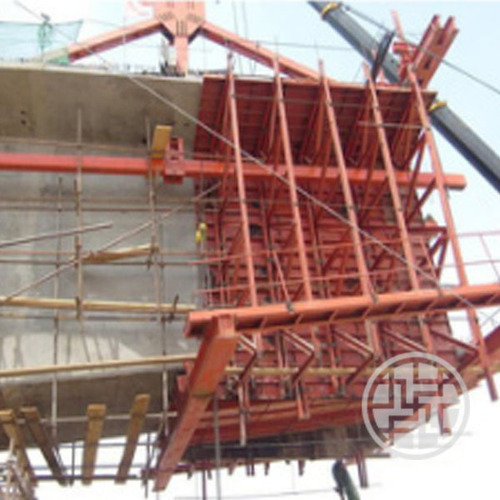
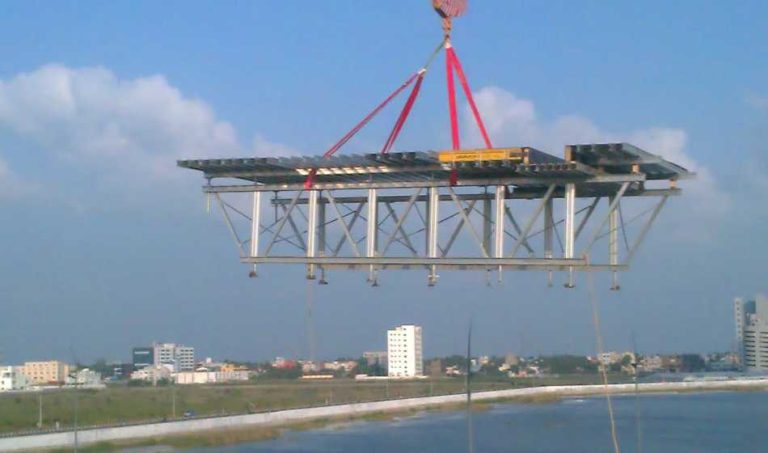
Panel systems: Big, ready-made panels for walls and floors.
Beam and slab systems are made to hold up horizontal constructions.
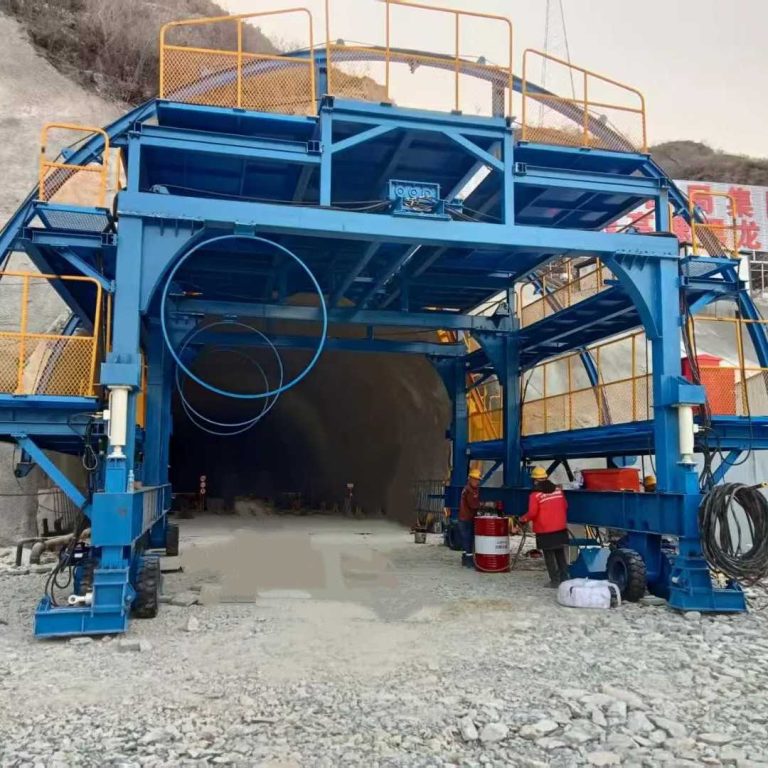
Tunnel formwork is an effective solution for repetitive projects like apartments or dorms.
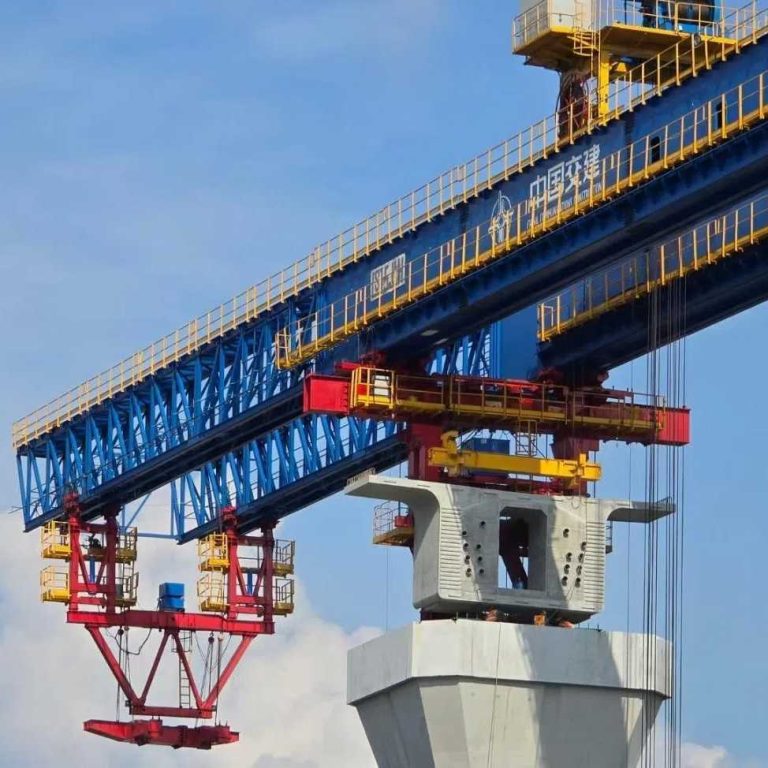
Climbing Formwork: This system is used in mid- to high-rise projects to facilitate vertical movement.
Each method makes things more efficient, but the expense depends on how complicated the job is.

What are three big reasons to use aluminum for building things?
Even though it has several problems, aluminum has some clear benefits:
Lightweight: This makes it easy to move and lowers shipping expenses.
High Reusability: If you take care of it, you can use it again and again, up to 150–200 times. This is good for the environment.
Smooth Finishes: Makes concrete surfaces clean, which lowers the expense of plastering and finishing.
These benefits are why builders keep using aluminum in the same types of projects over and over.
What are the risks of working with aluminum?
There are a number of dangers that come with using aluminum in construction:
Slippery Surfaces: When it rains, panels can become dangerous.
Sharp Edges—If you don’t handle them right, they can hurt you.
Problems with Fire Resistance: Aluminum loses strength when it becomes hotter beyond 400°C, which makes it dangerous during flames.
Deformation Under Load: If panels are too heavy, they may bend or break, putting workers in danger.
What Are the Drawbacks of Frames Made of Aluminum?
When aluminum is used in frames such as windows, doors, or formwork support, it presents certain problems:
Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum moves heat quickly, which makes buildings less energy efficient.
Corrosion in Some Places—Coastal or industrial areas are especially bad for this.
Aluminum expands a lot when the temperature changes, which can cause problems with the alignment of structures.
What Are the Issues with Aluminum Extrusion?
Aluminum extrusion is the process of shaping aluminum by pressing it through a mold. It makes things harder in construction formwork:
Dimensional Inconsistency: It’s challenging to get the right tolerances.
Surface Problems: You can see scratches, fissures, or uneven textures.
High Manufacturing Costs: Extrusion requires special tools, which makes aluminum formwork more expensive.
What Is the Quality of Aluminum Formwork?
6061 and 6082 are examples of 6000-series alloys that are often used in aluminum formwork. These alloys are chosen because they have:
- Ratio of strength to weight
- Good at not rusting
- Easy to make and weld
They work, but they are still not as strong as structural steel.
How to Use Aluminum Formwork
There is a set way to use aluminum formwork:
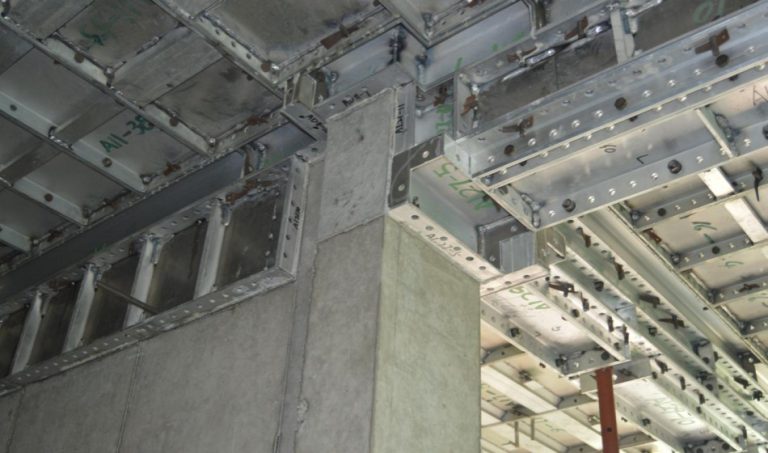
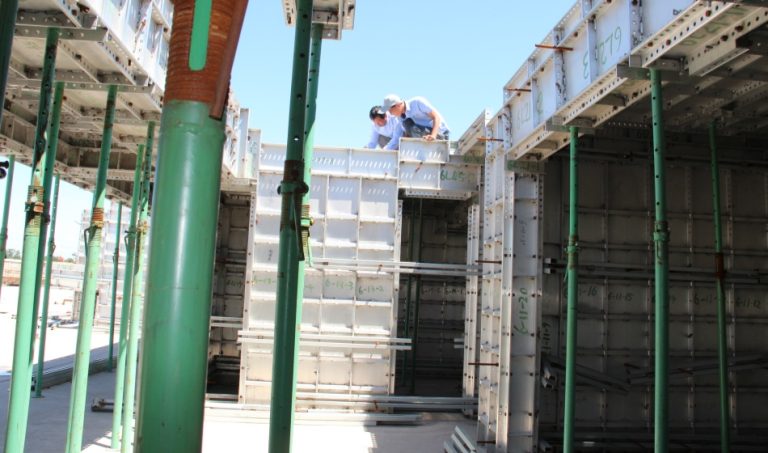
Design and Fabrication: Panels are made from architectural plans.
Assembly on Site: Pins and wedges are used to hold the panels together.
Pouring Concrete: The concrete is poured and then left to set.
Stripping: The panels are gently taken off when the concrete has set.
Reuse and Maintenance: The panels are cleaned, fixed if needed, and readied for the next cycle.
Planning carefully and hiring skilled workers are essential for efficiency.
What are the disadvantages of cast aluminum?
Some elements of formwork are made of cast aluminum, but it has some big flaws:
Porosity problems occur when small holes weaken the structure.
Cast aluminum is more prone to crack than forged aluminum.
Surface roughness needs to be smoothed after processing.
Questions and Answers About Aluminum Formwork
1.Is aluminum formwork stronger than steel?
Not always. Aluminum is lighter and easier to work with, whereas steel is stronger and lasts longer.
2.How often may aluminum formwork be used again?
With the right maintenance, they usually last for 150 to 200 cycles.
3.Can aluminum formwork be recycled?
Yes, it can be recycled 100%, which is good for the environment.
4.Is it possible to use aluminum formwork for tall buildings?
It’s good for buildings that are only a few stories tall, while steel is better for higher buildings that need to hold a lot of weight.
5.Could you please explain why aluminum formwork is so costly?
The high cost is due to the complicated ways of making things and the high cost of aluminum alloys.
6.What is the best way to care for aluminum formwork?
By cleaning it often, storing it correctly, and fixing damaged parts on time.
Conclusion
Aluminum formwork has changed the way we build today by making projects go faster and cutting down on waste. But it doesn’t work for everyone. Because of its high initial cost, lack of flexibility, structural problems, and safety issues, it isn’t right for every kind of project.
Aluminum formwork is great for big, recurring projects like housing estates because it gives great returns. But for projects with limited funds, unusual designs, or big loads, steel or wood might be better options.
If you’re considering aluminum formwork but worried about its disadvantages, exploring GOWE advanced formwork solutions can help you find a balance between innovation, safety, and cost-efficiency.